Restoring Mailbox Items in Exchange 2007
- This article is for Windows only
Summary:
It often happens that a mailbox or mailbox items such as emails or folders are accidentally deleted. Carbonite Safe Server Backup supports the restore of mailbox items back to user mailboxes in Microsoft Exchange 2007 in combination with native Exchange tools.
Note: Before restoring user mailboxes, verify if Exchange native tools can be used to restore the items.
When a user deletes items from the Deleted Items default folder by using the Delete, Shift+Delete, or Empty Deleted Items Folder actions, the items are moved to the Recoverable Items\Deletions folder. The duration that deleted items remain in this folder is based on the deleted item retention settings configured for the mailbox database or the mailbox.
By default, deleted items are kept for a period of 14 days, and deleted mailboxes are kept for 30 days.
The following Microsoft articles should help you restore items, if they are not purged from your mailbox database:
- How to search for deleted items in an Exchange mailbox (Opens new tab to Microsoft Knowledge Base)
- How can I recover items that I have "hard deleted" in Outlook? (Opens new tab to Microsoft Knowledge Base)
Solution:
The sections below are collapsed. Please click the section title to open / close a particular section.
Restoring Deleted Mailbox Items
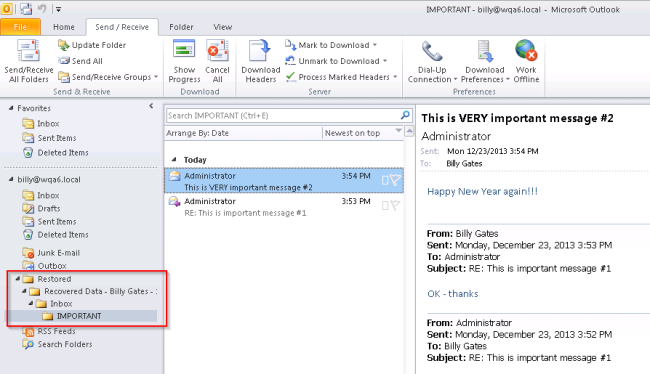
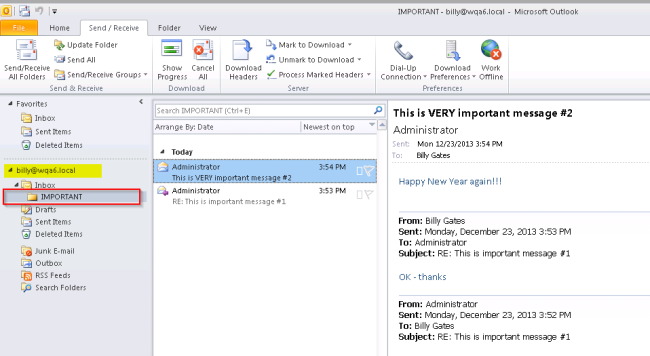
In this scenario, let's assume a user named Billy has accidentally deleted his IMPORTANT folder. By the time he discovered the folder was missing, the item had already been purged from the Recoverable Items folder.
To restore the deleted mail item(s), follow these steps.
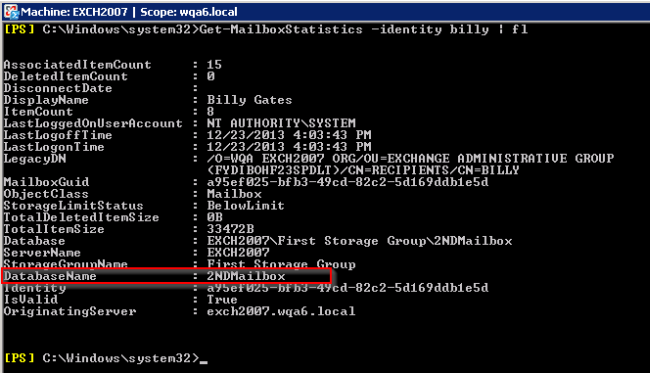
- Determine which database hosts the user's mailbox. If your environment uses a single mailbox for all users, skip this step.
If your environment uses multiple mailboxes, run the following command in the Exchange Management Shell (Powershell): Get-MailboxStatistics -identity [user] | fl, where [user] is "billy" in this case.
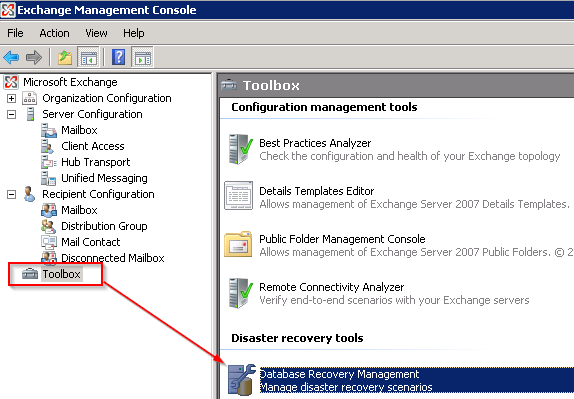
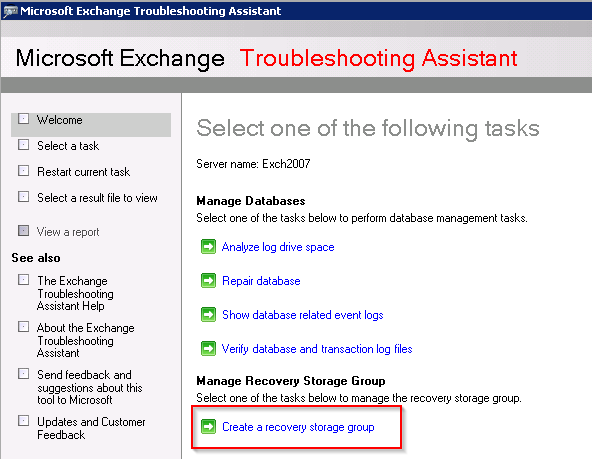
- Create a Recovery Storage Group using the Exchange Management Console (EMC) to use as temporary storage for the restored mailbox. Open the EMC, and click Database Recovery Management within the Toolbox node.
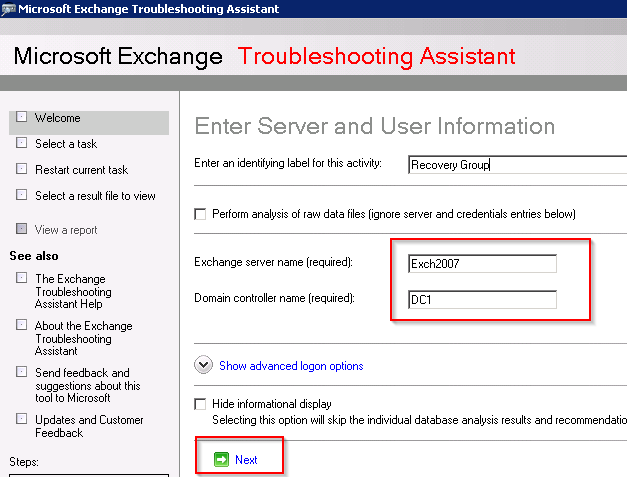
- Enter the names of your Exchange server and Domain Controller. Click Next to proceed.
- Within the Manage Recovery Storage Group section, click Create a Recovery Storage Group.
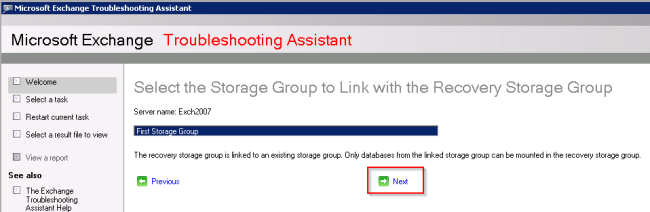
- After selecting the Storage Group you want to restore from, click Next.
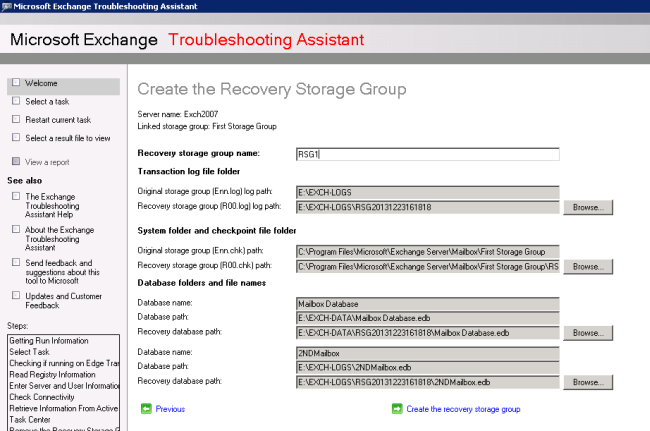
- Choose the location of the original Storage Group.
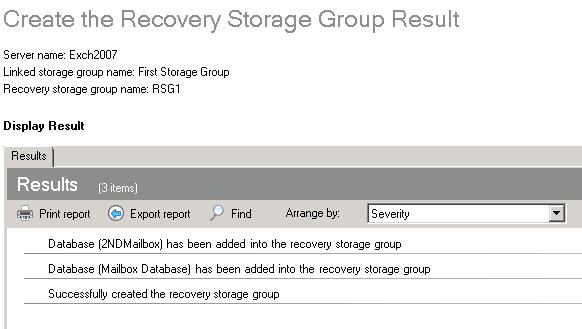
- Once the Recovery Storage Group has been successfully created, a window will appear.
- Launch Carbonite Safe Server Backup, and navigate to the Restore page. Select the backup run containing your mailbox database and restore to the Recovery Storage Group.
- Once the restore begins, you will be able to track the progress of your restore within the user interface.
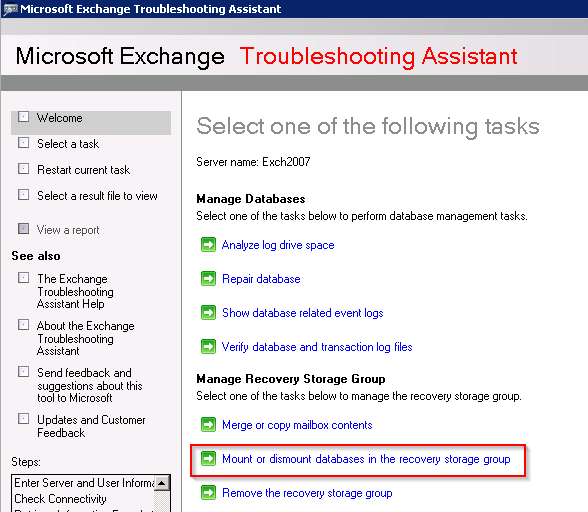
- Within the Exchange Management Console, select Mount or dismount databases in the recovery storage group.
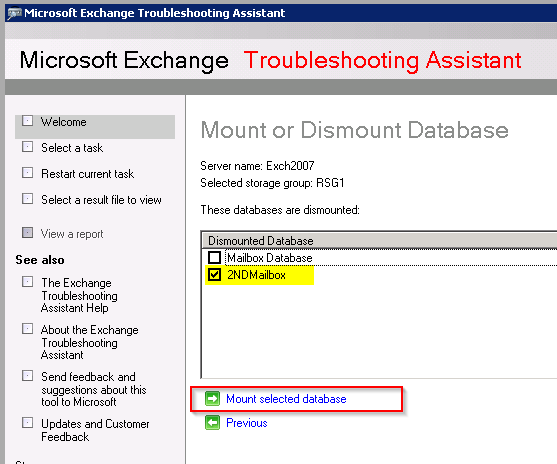
- Select your mailbox database and mount it.
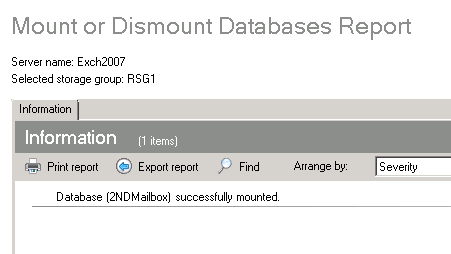
- Once the database has been successfully mounted or dismounted, a window will appear.
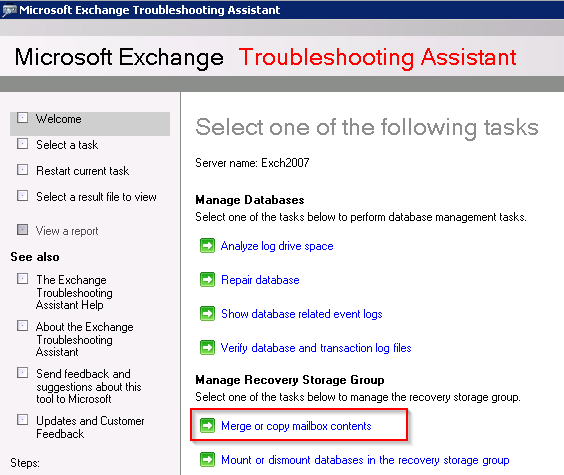
- Within the Manager Recovery Storage Group section, select Merge or copy mailbox content.
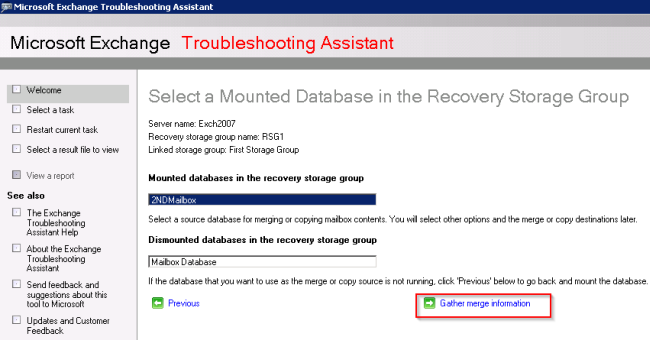
- Select the restored mailbox database, and click Gather merge information.
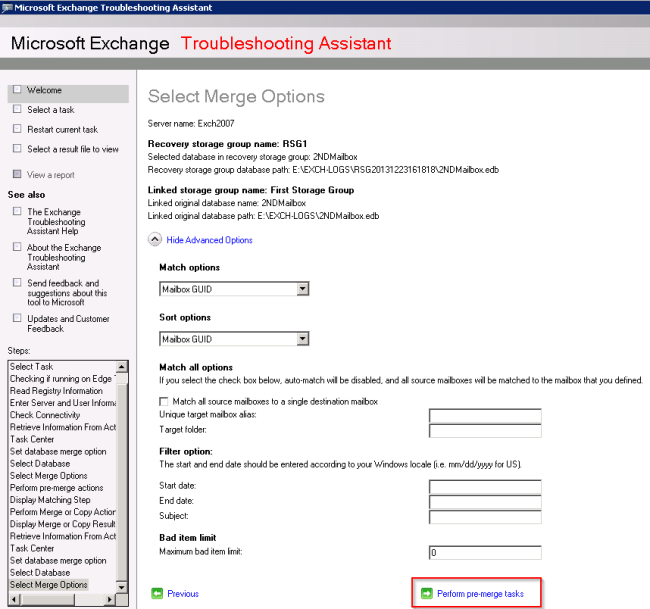
- After selecting your merge options, click Perform pre-merge tasks.
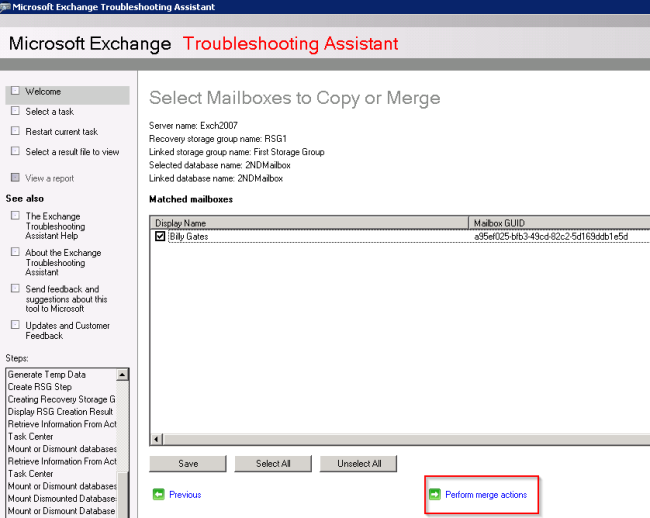
- A list of available mailboxes will be displayed. Ensure you have selected only the mailbox that you wish to recover items for, then click Perform merge action.
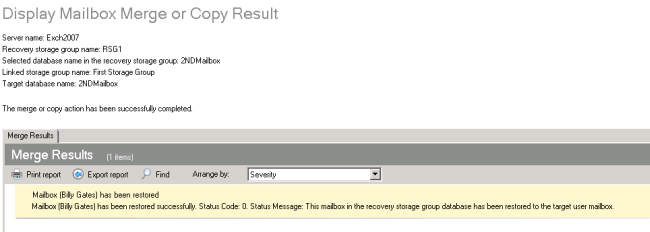
- Once the merge has been successfully completed, a window will appear.
- The items will be visible in the end user’s mailbox after the merge has completed.
Restoring Items Into a Sub-Folder of the User's Mailbox
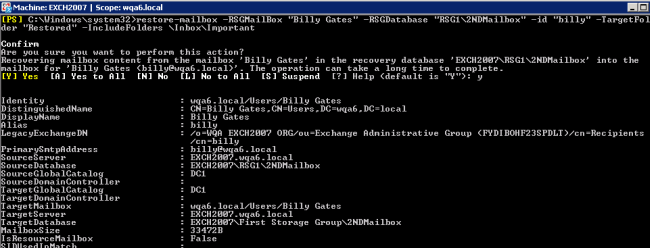
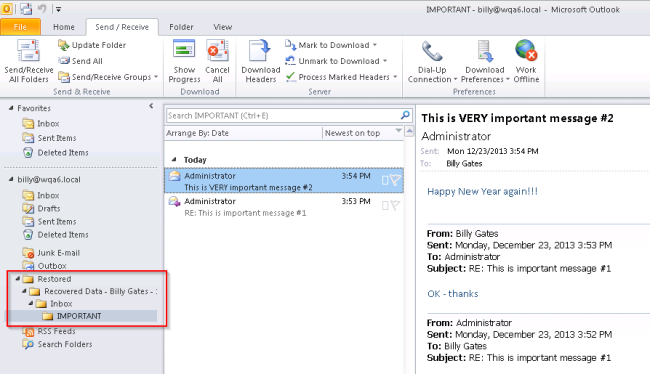
- We will use the Restore-Mailbox cmdlet A cmdlet is a lightweight command that is used in the Windows PowerShell environment. to restore mailboxes into the Restored folder. To restore the user's entire Inbox (including the Important folder) to a sub-folder named Restored, run the following command: restore-mailbox -RSGMailBox "Billy Gates" -RSGDatabase "RSG1\2NDMailbox" -id "billy" -TargetFolder "Restored" -IncludeFolders \Inbox\Important.
Note: If you want to perform a more granular restore, such as restoring messages with a specific subject, please refer to this article: Restore-Mailbox cmdlet.
- You can use Outlook to verify the contents of the restored mailbox.
In some scenarios, you might want restored items in the form of a PST file, rather than recovering them directly to a user mailbox. For example, let's assume you need to recover emails of an employee who is no longer with your organization.
You will have to create a temporary user with its own mailbox, recover email items to it, and then extract the recovered content to the PST file.
The following Microsoft Article will help you export a mailbox to a PST file: How to Export and Import mailboxes to PST files in Exchange 2007 SP1.
Performing Cleanup Operations
Once the mailboxes have been recovered, you should clean up any unnecessary databases, user accounts, and files.
- Dismount the recovery database and storage group. Delete files from database folders.
- If you used a temporary user for recovery, delete its mailbox and account in Active Directory along with any associated files (such as PSTs).




 Feedback
Feedback